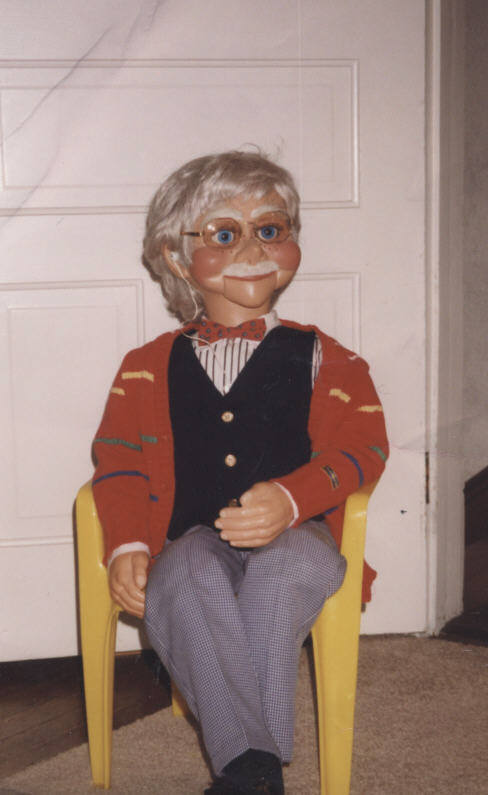
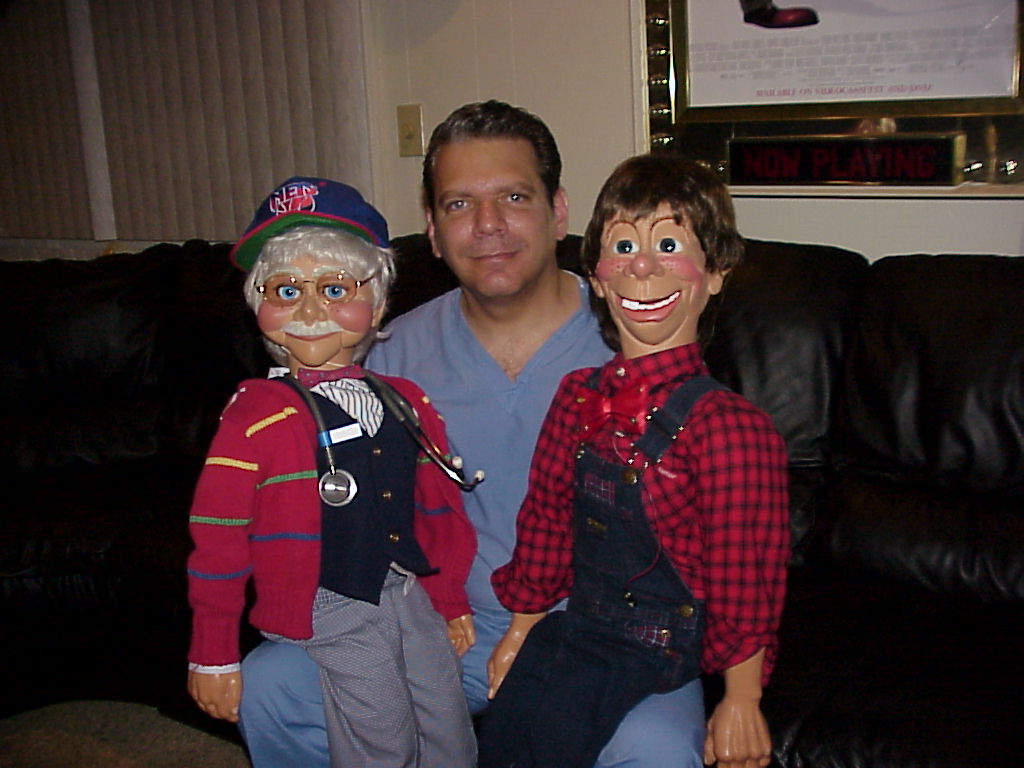
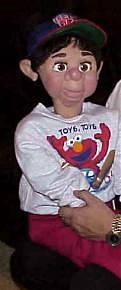
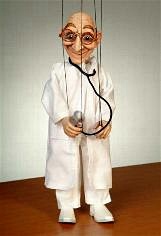
Dr. Gerard has utilized ventriloquist figures to teach medicine over many years, and recently incorporated marionette figures. They are used to teach individuals of any age about any medical condition, and can explain procedures in a way that anyone can understand. Dr. Gerard has 10 different original figures that can be utilized to accommodate different audiences.
It is now being recognized that there are better ways to learn than through the traditional methods. Institutions are beginning to show an increased awareness of the importance of the way individuals learn. Many of the standard methods utilized to convey knowledge have been shown to be relatively ineffective in an individuals ability to retain important concepts.
In many cases, learning tends to be passive and not active. The traditional methods of teaching do not allow individuals to have sufficient critical thinking.
The methods that Dr. Gerard utilizes for teaching medicine through ventriloquism makes teaching a personal experience, since it incorporates personal touches, communicates objectives clearly and creates a dynamic interactive learning environment to maximize learning with a practical learning experience. This method gives the patient the freedom to add vocal commentary. It makes certain that individuals know how to communicate their concerns.
Communication with the ventriloquist or marionette figure can assess what the patient already knows and then to ask questions to determine what the individual might be thinking. Not every individual is forthcoming with questions so the ventriloquist figure can help probe to discover the basic fears and concerns of the audience. Educating an audience with this technique will provide increased knowledge and understanding while at the same time decrease anxiety. The figure can also utilize open ended questions for the audience to convey areas of understanding. It engages psychological, social and medical needs, allowing an understanding of what is happening, what to expect and allows a partnership in successful treatment and disease prevention.
The use of simulation in teaching is an important teaching tool. It creates a convincing illusion that one is immersed in a virtual world. Simulating reality allows the audience to become participants and not just listeners or observers. It motivates the audience to get involved in the activity and creates greater interest in learning. The use of ventriloquist figures in teaching medicine can address any age group.
The use of ventriloquist or marionette figures are inspirational and they encourage enhancement of activity through ideas and they are empowering and therefore act as problem solving tools. They strive for realism, and thus create an overall feeling of reality, and inspire audience imagination.
In addition, humor is utilized with the ventriloquist and marionette figures to help in understanding of certain concepts. Dr. Lee Berk and fellow researcher Dr. Stanley Tan of Loma Linda University in California have been studying the effects of laughter on the immune system. To date their published studies have shown that laughter lowers the blood pressure, reduces stress hormones, increases muscle flexion, and boosts the immune function by raising levels of infection fighting T-cells, disease fighting proteins called Gamma interferon and B cells. Laughter also triggers the release of endorphins which produce a general sense of well being.
Dr. Gerard has used these figures to teach in schools, hospitals, nursing homes and they can be used just about anywhere to teach individuals about diseases, treatments and more important, disease prevention. He has developed teaching routines to discuss all of these concepts.
If you are interested in learning more about this form of creative medical teaching or for a demonstration or class at your institution, please contact Dr. Gerard at docnucs@yahoo.com
Dr. Gerard remains dedicated to the concept of Creative Medical Teaching, showing new creative innovative ways to teach patients, medical students, allied health professionals etc, about diseases and their treatments.